![[Group News] Leaders from Gansu Mobile Paid a Visit for Exchange and Guidance](/d/file/efpub/20250919/5e3579e7820f5f53c8128cbf6290f358.jpg)
In practical applications, we generally distinguish optical fiber connectors by their different structures. The following are some common optical fiber connectors currently available:
1. FC Type Optical Fiber Connector
This type of connector was first developed by NTT of Japan. FC is the abbreviation of Ferrule Connector, indicating that its external reinforcement method adopts a metal sleeve and the fastening method is a screw thread. Initially, FC-type connectors used ceramic ferrules with a flat contact end face (FC). Such connectors have a simple structure, easy operation, and are easy to manufacture, but the fiber end face is sensitive to microdust, prone to Fresnel reflection, and it is difficult to improve return loss performance. Later, this type of connector was improved by using ferrules with a spherical end face (PC) without changing the external structure, which significantly improved insertion loss and return loss performance.
2. SC Type Optical Fiber Connector
This is an optical fiber connector developed by NTT Corporation of Japan. Its shell is rectangular, and the structural dimensions of the ferrule and coupling sleeve used are exactly the same as those of the FC type. The end face of the ferrule mostly adopts PC or APC polishing; the fastening method is a plug-in latch type without rotation. Such connectors are low-cost, easy to plug and unplug, have small fluctuations in insertion loss, high compressive strength, and high installation density.
ST and SC interfaces are two types of optical fiber connectors. For 10Base-F connections, the connector is usually of ST type; for 100Base-FX, the connector is mostly of SC type. The core of the ST connector is exposed, while the core of the SC connector is inside the joint.
3. Biconic Connector
The most representative product of this type of optical fiber connector was developed by Bell Labs in the United States. It consists of two cylindrical plugs with precision-molded truncated conical ends and a coupling assembly with a biconical plastic sleeve inside. DIN47256 type optical fiber connector This is a connector developed in Germany. The structural dimensions of the ferrule and coupling sleeve used in this connector are the same as those of the FC type, and the end face is processed by PC polishing. Compared with FC-type connectors, its structure is more complex, and there is a spring controlling pressure in the internal metal structure, which can avoid damage to the end face due to excessive insertion pressure. In addition, this type of connector has high mechanical precision, so the insertion loss value is small.
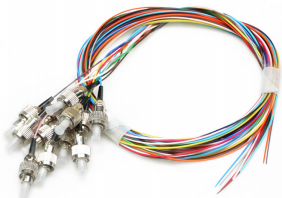
4. MT-RJ Type Connector
MT-RJ originated from the MT connector developed by NTT. It has the same latching mechanism as the RJ-45 type LAN electrical connector. The optical fibers are aligned through guide pins installed on both sides of the small sleeve. To facilitate connection with optical transceivers, the optical fibers on the connector end face are designed in a dual-core (0.75mm spacing) arrangement. It is a next-generation high-density optical fiber connector mainly used for data transmission.
5. LC Type Connector
The LC type connector was developed by the famous Bell Labs and is made using an easy-to-operate modular jack (RJ) latching mechanism. The size of the ferrule and sleeve used is half of that of ordinary SC, FC, etc., which is 1.25mm. This can increase the density of optical fiber connectors in the optical fiber distribution frame. Currently, in terms of single-mode SFF, LC-type connectors have actually occupied a dominant position, and their application in multi-mode is also growing rapidly.
6. MU Type Connector
The MU (Miniature Unit Coupling) connector is based on the most widely used SC-type connector and is the world's smallest single-core optical fiber connector developed by NTT. This connector adopts a 1.25mm diameter sleeve and a self-retaining mechanism, and its advantage is that it can achieve high-density installation. Using the 1.25mm diameter sleeve of MU, NTT has developed a series of MU connectors. They include socket-type connectors for optical cable connection (MU-A series); backplane connectors with self-retaining mechanism (MU-B series); and simplified sockets for connecting LD/PD modules and plugs (MU-SR series), etc. With the rapid development of optical fiber networks towards larger bandwidth and higher capacity and the wide application of DWDM technology, the demand for MU-type connectors will also grow rapidly.
7. Others
Optical fiber connector can also refer to FICON—FIber Connector, a mainframe channel launched by IBM in 1998 together with G5 servers. Based on the Fibre Channel standard, it increases the half-duplex 17MB/s transmission rate of ESCON to full-duplex 100MB/s. Each FICON channel can support up to 4,000 I/O operations per second, equivalent to 8 ESCON channels.
——END——
